Simple Random Sampling Method Example | We record one or more of its properties (perhaps its color, number. Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article, probability sampling, if you do not know what probability sampling is. In this method, the researcher gives each member of the population a number. One way would be the lottery method. Simple random samples are usually representative of the population we're interested in since every member has an equal chance of being included in this type of sampling method is sometimes used because it's much cheaper and more convenient compared to probability sampling methods.
'simple random sampling' is the simplest method of sampling for social research experiments. The example in which the names. In the lottery method, you choose the. Each of the n population members is assigned a. Stratified sampling would be preferred over cluster sampling, particularly if the questions of interest are affected by time zone.

In statistics, a simple random sample is a subset of individuals (a sample) chosen from a larger set (a population). Probability sampling procedures must meet 4 criteria (chochran, 1977:9): We can define the set of distinct samples which the procedure is capable of selecting. One way would be the lottery method. The lottery or random number method. With the simple random sample, there is an equal chance (probability) of selecting each unit from the population being studied when creating. Stratified sampling would be preferred over cluster sampling, particularly if the questions of interest are affected by time zone. If you're dealing with a huge or widely distributed population, simple or stratified sampling can be difficult or impossible. There are definitions, simple examples, somewhat more complicated examples, and reasoning behind why we use this method. In other words, the sample has a known probability. Simple random sampling (also referred to as random sampling) is the purest and the most straightforward probability sampling strategy. Poor method application will simple random sampling works best when you can manage a small percentage of the overall demographic. For example, a simple random sample, probability proportional to sample size etc.
Simple random sampling is a fundamental sampling method and can easily be a component of a more complex sampling method. If you're dealing with a huge or widely distributed population, simple or stratified sampling can be difficult or impossible. This can be done in one of two ways: In the lottery method, you choose the. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something.
For example to do a true random sample of the population of the usa, you would start with a list of everyone there, then select a. Simple random sampling is the most basic and common type of sampling method used in quantitative social science using the same example above, let's say we put the 100 pieces of paper in a bowl, mix them up, and randomly. Here, sample is selected according to a quota system. Each of the n population members is assigned a. In statistics, a simple random sample is a subset of individuals (a sample) chosen from a larger set (a population). In the example used in the introduction. A textbook example of simple random sampling is sampling a marble from a vase. Probability sampling procedures must meet 4 criteria (chochran, 1977:9): Methodology is vital to getting a truly random sample. Simple random sampling is basic method of sampling. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. 'simple random sampling' is the simplest method of sampling for social research experiments. Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article, probability sampling, if you do not know what probability sampling is.
In probability sampling methods, it is possible to both determine which sampling units belong to which sample and the probability that each sample will be selected. A sample is called simple random sample if each unit of the population has an equal chance of being another way of defining a simple random sample is that if we consider all possible samples of the following methods are used for the selection of a simple random sample: This packet introduces you to the concept of simple random sampling. Random samples are the best method of selecting your sample from the population of interest. I am using sample_n(df, replace = true, n) from dplyr to reduce the size and have a better fit.
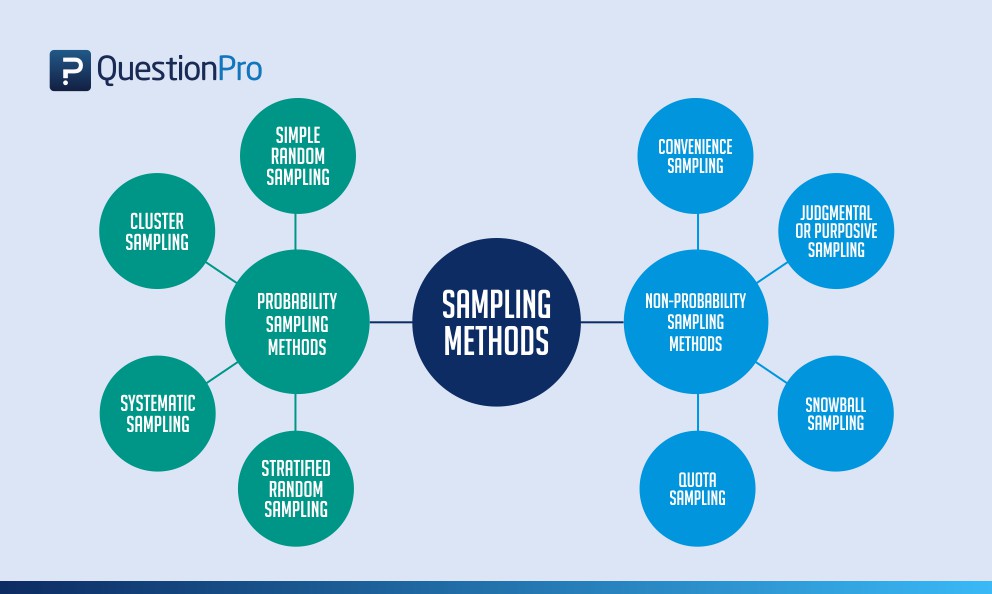
Here, sample is selected according to a quota system. Random samples are the best method of selecting your sample from the population of interest. Find simple random sampling examples types of random sampling. 'simple random sampling' is the simplest method of sampling for social research experiments. The lottery or random number method. In other words, the sample has a known probability. The most primitive and mechanical would be the lottery method. A textbook example of simple random sampling is sampling a marble from a vase. It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen. I am using sample_n(df, replace = true, n) from dplyr to reduce the size and have a better fit. One way would be the lottery method. For example, students studying english literature may spend more money on books than engineering students so if we use a very large percentage of english students or engineering students then our. If you're dealing with a huge or widely distributed population, simple or stratified sampling can be difficult or impossible.
It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen random sampling method example. I am using sample_n(df, replace = true, n) from dplyr to reduce the size and have a better fit.
Simple Random Sampling Method Example: With a lottery method, each member of the population is assigned a number, after which numbers are selected at random.
Fonte: Simple Random Sampling Method Example
comment 0 Comments
more_vert